Table of Contents
ToggleSilicone is a versatile synthetic material known for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat and chemicals. It is widely used in medical devices, automotive parts, electronics, cookware, and baby products. But have you ever wondered—how is silicone produced?

This article will take you through the complete process of silicone manufacturing, from raw materials to finished components, and explain why it is such a vital material across industries.
1. What Is Silicone?
Silicone is a polymer made from silicon (Si), oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. It’s not the same as silicon, the natural element. Instead, it combines inorganic silica (from sand) with organic functional groups, giving it unique physical properties.
2. Raw Material: Silica (Quartz Sand)
The primary raw material for it is silica (SiO₂)—a naturally occurring substance found in sand, quartz, and rocks. The process begins with high-purity quartz sand, which contains over 99% silicon dioxide.
Step 1: Mining and purification
- Quartz is mined and refined into ultra-pure silica.
- Impurities like metal oxides are removed to prepare it for chemical reactions.
3. Silicon Metal Production
To create silicone, pure silicon metal must first be extracted from silica.
Step 2: High-temperature reaction
Silica is heating with carbon (usually coal or wood chips) at temperatures around 1800°C in an electric arc furnace.
Chemical reaction:
SiO₂ + 2C → Si (metallic silicon) + 2CO (gas)
The result is metallurgical-grade silicon, which forms the foundation of lsr production.
4. Synthesis of Chlorosilanes
Step 3: Reacting silicon with methyl chloride (CH₃Cl)
Silicon metal is reacting with methyl chloride in the presence of a copper catalyst at 300°C. This produces methylchlorosilanes, especially dimethyldichlorosilane (DMDCS).
Reaction:
Si + CH₃Cl → (CH₃)₂SiCl₂ (main product)
This stage is crucial because chlorosilanes are the building blocks for silicone polymers.
5. Hydrolysis and Polymerization
Step 4: Hydrolysis
Chlorosilanes are then mixed with water, leading to hydrolysis. The chlorine atoms are replacing with hydroxyl groups, which react to form siloxane bonds (Si-O-Si)—the backbone of silicone.
Step 5: Polymerization
Through controlled polymerization, manufacturers produce different types of silicone:
- Short-chain siloxanes → Silicone oils
- Long-chain siloxanes → Silicone elastomers (rubber)
- Cross-linked structures → Silicone resins

6. Compounding and Formulation
At this stage, additives are introducing depending on the application:
- Curing agents (platinum, peroxide)
- Colorants
- Reinforcing fillers (like fumed silica for strength)
The silicone compound is now ready for shaping and molding.
7. Curing and Processing (Heat or Platinum-Cured)
It can be processing into final parts through several methods:
- LSR Injection Molding (Liquid Silicone Rubber)
- Compression molding
- Extrusion for tubes and profiles
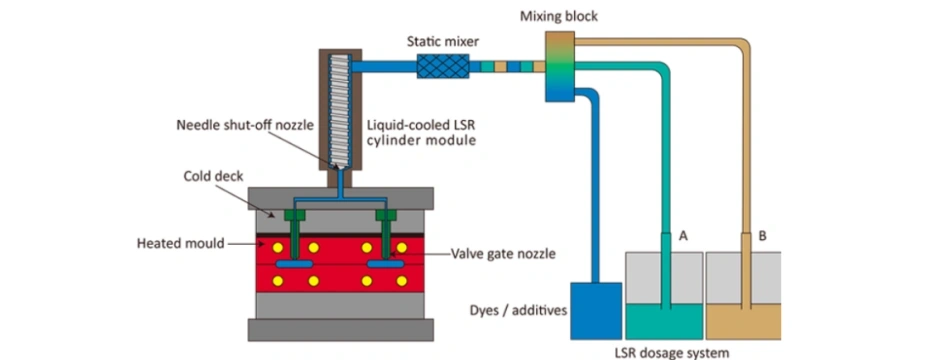
Curing Methods:
- Heat-Cured Silicone (HCR): Requires heat and peroxide catalysts
- Platinum-Cured Silicone: Faster, cleaner, ideal for medical and food-grade products
8. Post-Curing and Quality Testing
Post-curing involves heating the lsr product at high temperatures (usually 200°C) to remove volatile substances and enhance mechanical properties. Then, the products undergo:
- Tensile and hardness testing
- Biocompatibility testing (for medical-grade)
- Dimensional and visual inspection
9. Final Products and Applications
After molding and testing, It is using to manufacture a wide range of products:
- Medical devices (catheters, CPAP masks)
- Consumer goods (bottle nipples, bakeware)
- Automotive parts (gaskets, seals)
- Electronics (keypads, potting materials)
Its durability, flexibility, and thermal resistance make it indispensable in modern life.

Conclusion
Silicone is easy to customize and mold and comes in a variety of forms (liquid, solid or sheet) depending on the molding or fabrication process and specific use. Whether your application requires greater temperature resistance or more malleability, material manufacturers offer a variety of compounds and grades to meet your various needs.
Turn to JIAZE Silicone Parts for Liquid Silicone Rubber Molded Components
At Jiaze, we believe in providing our customers with value-added solutions. These solutions utilize the best-suited material, tooling and manufacturing process that will deliver high-performance liquid silicone rubber injection molded parts and extraordinary results.

Our LSR injection molding cells incorporate precision automation, innovative technology, a stable process and rigorous quality standards, inspections and testing to ensure we meet the highest quality possible customized for your specific requirements. We strive to deliver precision, value-added LSR components that consistently meet our customer’s productivity, cost, and quality objectives.