Table of Contents
ToggleLiquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) has revolutionized product design in sectors like medical devices, baby products, automotive components, and electronics. Its ability to be injection molded into complex shapes with high precision makes it ideal for custom parts.

Custom injection molded LSR parts offer high consistency, chemical resistance, thermal stability, and biocompatibility—making them especially popular in regulated industries. But to get the best results, you need to understand the full customization process, from material selection to mold design, tooling, and production.
1. What Is Injection Molded LSR?
Injection molded LSR parts are made from two-part platinum-cured silicone that is injected into a mold under high pressure and heat. The LSR material cures inside the mold, forming flexible, durable components with high repeatability.
Key Characteristics:
- High thermal resistance (-50°C to 250°C)
- Excellent chemical and UV resistance
- Biocompatible and hypoallergenic
- Low compression set
- Suited for high-volume production
Industries that benefit include:
- Medical: Catheters, valves, seals
- Consumer: Baby nipples, kitchenware
- Automotive: Seals, connectors, boots
- Electronics: Gaskets, covers, membranes
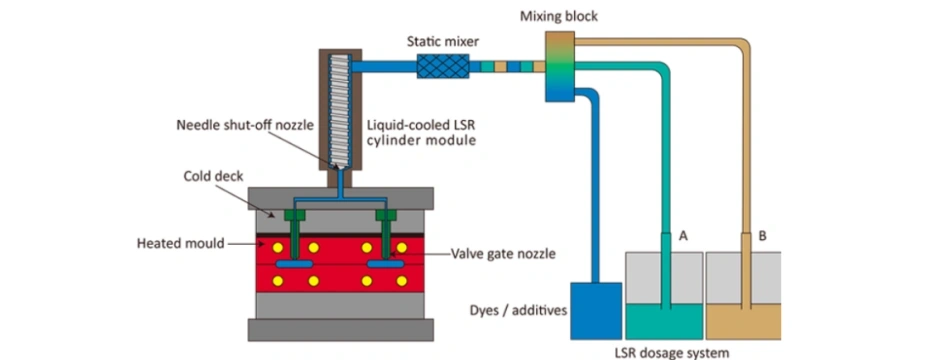
2. Benefits of Custom Injection Molded LSR Parts
Custom LSR parts offer precise fit, unique geometries, and optimized performance for specific use cases.
Advantages:
- Design Flexibility: Thin walls, undercuts, complex geometry
- Material Purity: Ideal for FDA, ISO 10993, USP Class VI standards
- Automated Production: Reduces labor and human error
- Fast Cycle Times: Rapid curing speeds
- Multi-shot Compatibility: Can be overmolded on plastics or metals
3. Step-by-Step: How to Custom Injection Molded LSR Parts
Step 1: Define Part Requirements
Start with understanding the functional, mechanical, and regulatory requirements. Ask questions like:
- Will it contact food or skin?
- What are the required tolerances?
- What temperature or chemical resistance is needed?
- Is transparency or color matching necessary?
Step 2: Choose the Right LSR Grade
LSR comes in many grades. Choose based on:
- Medical or Food Grade (for safety-critical parts)
- Flame Retardant Grades (for automotive and electronics)
- Self-lubricating LSR (for dynamic parts like valves or seals)

Step 3: Part Design for LSR Injection Molding
Use DFM (Design for Manufacturability) principles. Key considerations:
- Draft Angles: For easy demolding
- Uniform Wall Thickness: Reduces shrinkage
- Avoid Sharp Corners: Use radii to improve flow
- Venting & Flow Channels: Improve filling and curing
- Parting Line Optimization: To avoid flash on visible areas
Design using CAD tools, and simulate with mold flow analysis.
Step 4: Tooling Design & Mold Fabrication
Mold tooling is a crucial part of custom LSR injection molding. It’s typically made from hardened steel or aluminum.
Mold considerations:
- Cold Runner vs Hot Runner: Cold runners are common for LSR
- Number of Cavities: Depends on production volume
- Mold Material: Choose based on expected tool life
- Venting: Essential to release trapped air
- Shut-offs & Inserts: Help create complex shapes and overmolding
Tooling lead time: 3–6 weeks depending on complexity.
Step 5: Prototype & Testing
Before full-scale production:
- Create prototype molds or 3D printed LSR-like parts
- Perform mechanical and chemical tests
- Validate material performance, sealing, color, durometer, and biocompatibility
- Make revisions based on results

Step 6: Mass Production
Once the mold is approved, move to production using automated LSR injection molding machines.
Production includes:
- Material Mixing: Two-part LSR is precisely metered
- Injection: Injected into mold under controlled pressure
- Curing: Heat initiates fast platinum-catalyzed curing
- Demolding: Fully cured part is ejected automatically
- Inspection: Visual, dimensional, and performance testing
4. Cost Factors for Custom LSR Molding
Cost is affected by multiple variables:
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
| Mold Complexity | Higher complexity = higher tooling cost |
| Material Grade | Medical/Food grade costs more |
| Part Size | Larger parts use more material |
| Cavities in Mold | More cavities = higher mold cost but lower unit price |
| Volume | Higher quantities reduce unit cost |
| Secondary Processes | Trimming, post-curing, assembly may add costs |
Pro tip: For long-term projects, the upfront tooling cost pays off with lower per-part pricing.
5. Quality Control & Compliance
Ensure parts meet the highest standards through:
- ISO 13485 Certification (for medical parts)
- FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 Compliance (for food contact)
- RoHS/REACH Compliance (for electronics)
Tests include:
- Tensile strength
- Compression set
- Tear resistance
- Biocompatibility (ISO 10993, USP Class VI)
- Visual inspection for flash or warping

6. Applications of Custom Injection Molded LSR Parts
Medical Devices
- Respirator masks, gaskets, syringes, pump valves
Automotive
- Connector seals, wiring boots, sensor grommets
Consumer Goods
- Wearables, baby bottle nipples, kitchen tools
Electronics
- Waterproof buttons, phone gaskets, LED diffusers
7. Finding a Reliable LSR Molding Partner
Choosing the right manufacturer is critical. Look for:
- Proven LSR experience
- In-house mold design and production
- Cleanroom manufacturing capabilities
- ISO-certified quality management systems
- Fast prototyping and lead times
Conclusion
Custom injection molded LSR parts offer unbeatable performance, reliability, and flexibility for a wide range of industries. Whether you’re developing a new medical device or sealing component for automotive use, understanding the design, tooling, material, and production process is the key to success.

By partnering with an experienced LSR injection molding expert and following proper design and material guidelines, your custom part will be cost-effective, compliant, and high-performing.