Table of Contents
ToggleSilicone injection molding has become a leading process for creating precision silicone parts used in various industries such as medical devices, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. Custom silicone injection molded parts are known for their high durability, flexibility, and resistance to extreme temperatures, making them essential for numerous applications.
This guide provides an in-depth look at how to custom silicone injection molded parts, from initial design to final production.
1. Understanding Silicone Injection Molding
Before diving into the steps to create custom silicone injection molded parts, it’s essential to understand the basics of silicone injection molding. This process involves injecting liquid silicone rubber (LSR) into a mold cavity under high pressure, where it then cures and solidifies to form the desired part. The process is efficient and cost-effective, making it ideal for producing large volumes of identical parts with precise dimensions and high-quality surface finishes.
Key Advantages:
- High Precision: Silicone injection molding can produce parts with extremely tight tolerances.
- Durability: LSR offers resistance to heat, chemicals, and wear, making it ideal for demanding environments.
- Flexibility: Silicone can be molded into complex shapes and is available in a range of hardness and flexibility.
2. Step-by-Step Process for Custom Silicone Injection Molding
Step 1: Designing the Silicone Mold
The first step in creating custom silicone injection molded parts is designing the mold. The mold design must consider factors like the part’s functionality, material properties, and ease of injection. When designing, it is important to collaborate with experienced mold designers to ensure the mold is durable and efficient.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate silicone material (e.g., medical-grade, food-grade, or industrial-grade) based on the application.
- Mold Features: The mold should have the right number of gates, vents, and runners to ensure a smooth flow of silicone.
- Parting Line: The parting line (where the two halves of the mold meet) should be strategically placed to minimize visible marks on the part.
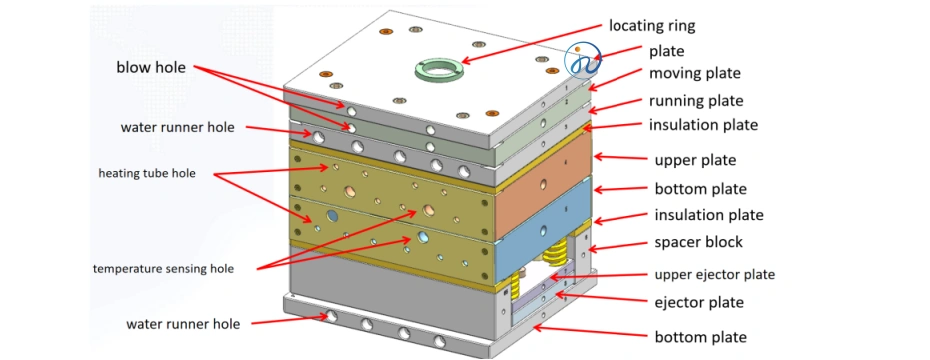
Step 2: Material Selection for Custom Silicone Injection Molding
Selecting the right silicone material is crucial for the performance and longevity of the final product. Common options include:
- Medical-Grade Silicone: Suitable for parts that will come into contact with the human body (e.g., CPAP masks, baby products).
- Food-Grade Silicone: Used for products in the food industry, such as bakeware or utensils.
- Industrial-Grade Silicone: Ideal for products requiring high durability, such as gaskets, seals, and automotive parts.
Work with your supplier to choose the right silicone formulation based on factors like temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and flexibility.

Step 3: Mold Fabrication
Once the design is complete and the material has been selected, the next step is mold fabrication. This step involves creating the actual mold that will hold the silicone material during injection.
- Mold Materials: Typically, molds are made of steel or aluminum, with steel offering better durability and heat resistance.
- Cavity Design: The number of cavities in the mold determines the production rate. Multi-cavity molds are ideal for high-volume production.
- Mold Temperature Control: Proper temperature regulation ensures consistent curing of the silicone material.
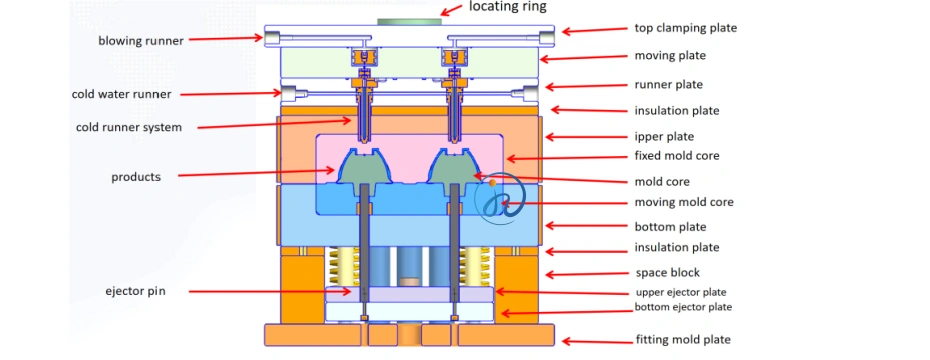
Step 4: Injection Molding Process
During the injection molding process, the liquid silicone rubber is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is then heated to allow the silicone to cure and solidify, taking the shape of the mold.
- Injection Pressure: The pressure must be optimized to ensure the silicone flows smoothly and fills the mold without air pockets or defects.
- Curing Time: The curing time depends on the type of silicone used, but it generally ranges from 30 seconds to a few minutes.
- Cooling: After curing, the mold is cooled to allow the silicone part to solidify further before removal.
Step 5: Post-Processing and Finishing
Once the silicone parts are removed from the mold, they may undergo several post-processing steps to achieve the final product. This could include:
- Trimming: Removing excess silicone, also known as flash, from the part.
- Cleaning: Parts are cleaned to remove any residual oils or mold release agents.
- Surface Finishing: Some parts may require additional surface treatments, such as printing, coating, or texturing.
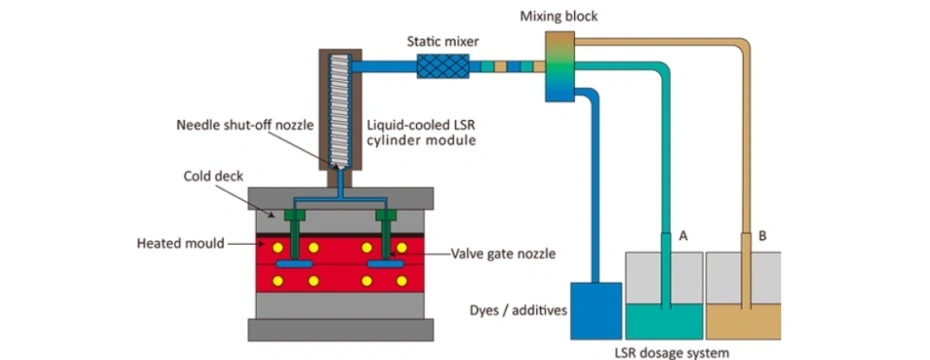
Step 6: Quality Control and Testing
Before the parts are shipped to customers, they must undergo rigorous quality control and testing to ensure they meet the required specifications. This may involve:
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifying the part dimensions against the design specifications.
- Material Testing: Checking the silicone material for hardness, tensile strength, and elasticity.
- Functional Testing: Testing the part in its intended application to ensure it performs correctly.
3. Benefits of Custom Silicone Injection Molded Parts
- Consistency: Silicone injection molding offers high repeatability, ensuring each part meets the same standards.
- Complex Geometries: Custom parts with intricate details and shapes can be molded easily.
- Cost-Efficiency: Although mold production may involve an initial investment, high-volume production reduces per-unit costs.
- Variety of Applications: Silicone injection molded parts are used in medical devices, automotive, electronics, and consumer products, providing versatile solutions.
4. Applications of Custom Silicone Injection Molded Parts
- Medical Devices: Silicone is biocompatible, making it an ideal material for medical applications such as catheters, gaskets, and seals.
- Consumer Goods: Products like kitchenware, baby products, and personal care items benefit from the durability and flexibility of silicone.
- Automotive: Silicone gaskets, seals, and electrical components are critical in automotive manufacturing due to silicone’s heat and chemical resistance.
- Electronics: Silicone is used in electrical insulation, protective covers, and sealing components in consumer electronics.

5. Challenges in Silicone Injection Molding
While silicone injection molding offers many advantages, there are challenges that manufacturers need to be aware of:
- High Initial Costs: The cost of mold design and fabrication can be significant, especially for complex parts.
- Material Limitations: Silicone may not be suitable for all applications, especially where high-strength or specific chemical resistance is required.
- Cycle Time: Although silicone curing is fast, cycle times may still be longer compared to other plastics.
Conclusion
Custom silicone injection molded parts offer unmatched precision, durability, and versatility for various industries. By following the outlined process—starting from mold design to material selection, molding, post-processing, and quality testing—you can produce high-quality, reliable silicone parts tailored to your needs.

Whether you are in the medical, automotive, or consumer goods sector, silicone injection molding can help you create innovative solutions that meet the highest standards of performance and quality.