Table of Contents
ToggleLiquid Silicone Rubber molding manufacturing is a highly automated and precise production process used to create flexible, durable, and high-performance silicone parts. Due to its excellent biocompatibility, heat resistance, and chemical stability, LSR molding is widely used in medical, automotive, electronics, and consumer products.
1. What Is LSR Molding Manufacturing?
LSR molding manufacturing is a liquid injection molding process that transforms two-part liquid silicone rubber into finished elastomeric parts through controlled mixing, injection, heating, and curing inside a precision mold.
Unlike solid rubber or thermoplastic molding, LSR manufacturing relies on:
- Low-viscosity liquid materials
- Platinum-catalyzed curing
- Heated molds instead of cooling
- Fully automated production systems
The result is consistent, flash-free, and high-precision silicone components.

2. Materials Used in LSR Molding Manufacturing
2.1 Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
LSR consists of two components:
- Part A: Silicone base with catalyst
- Part B: Silicone base with crosslinker
They are mixed in a 1:1 ratio before injection.
Key Properties of LSR:
- Excellent elasticity
- High temperature resistance (−50°C to 200°C)
- Chemical and UV resistance
- Biocompatibility (medical-grade available)
2.2 Additives and Pigments
Depending on application requirements, LSR manufacturing may include:
- Color pigments
- Self-lubricating additives
- Flame retardants
- Conductive or insulating fillers

3. Equipment Required for LSR Molding Manufacturing
LSR molding requires specialized equipment different from standard plastic injection molding.
3.1 LSR Injection Molding Machine
Key features:
- Precision metering pumps
- Static or dynamic mixing unit
- Closed-loop control system
- Injection pressures up to 200 bar
3.2 Cold Runner System
The cold runner keeps LSR in a liquid state before entering the mold, preventing premature curing and reducing material waste.
3.3 Heated Mold System
Molds are heated to 160–200°C to activate vulcanization and ensure complete curing.
3.4 Automation & Robotics
Many LSR manufacturing lines integrate:
- Robotic demolding
- Automated inspection
- Inline trimming systems
4. Mold Design for LSR Molding Manufacturing
Mold design is one of the most critical factors in successful LSR molding.
4.1 Mold Material
Common choices include:
- H13 tool steel
- S136 stainless steel (medical & food-grade)
- NAK80 for high polish requirements
4.2 Cavity and Parting Line Design
Because LSR flows easily, parting lines must be extremely precise to prevent flash. Tolerances are typically within ±0.005 mm.
4.3 Venting Design
Micro-vents allow trapped air to escape:
- Vent depth: 0.003–0.01 mm
- Prevents air bubbles and short shots
4.4 Gate Design
Common gate types:
- Valve gates
- Pin gates
- Sub-gates
Gate placement affects flow balance and surface appearance.
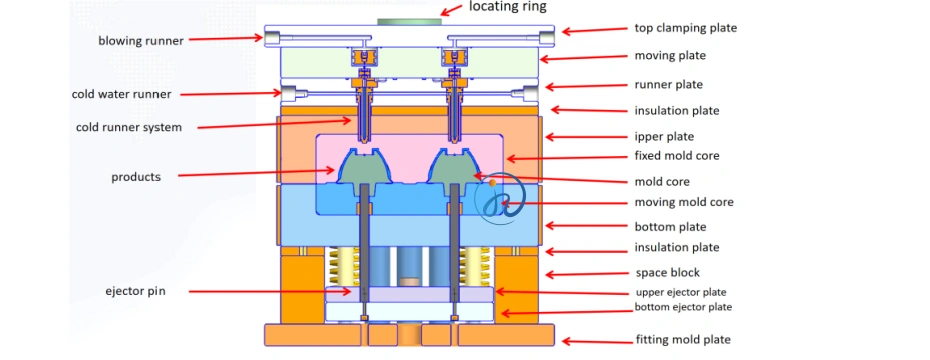
5. Step-by-Step LSR Molding Manufacturing Process
Step 1: Material Storage and Feeding
LSR Part A and Part B are stored in sealed containers and fed into metering pumps to avoid contamination.
Step 2: Precise Metering and Mixing
The two components are mixed at a 1:1 ratio. Accurate mixing is essential for:
- Consistent curing
- Mechanical strength
- Surface quality
Step 3: Injection into Mold
The mixed LSR is injected through the cold runner into the heated mold cavities under controlled pressure.
Step 4: Curing and Vulcanization
Once inside the heated mold, LSR cures rapidly through platinum-catalyzed crosslinking.
Typical curing time:
- 20–60 seconds (depending on part thickness)
Step 5: Demolding
Due to LSR’s flexibility:
- Parts can be demolded easily
- Ejector pins may not be required
- Robotic removal is common
Step 6: Post-Processing (If Required)
LSR molding often produces finished parts directly, but optional steps include:
- Trimming (minimal flash removal)
- Post-curing (rare, for specific specs)
- Surface inspection
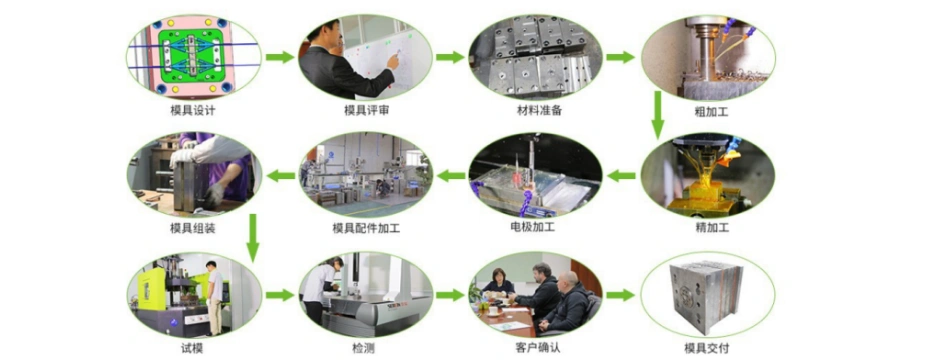
6. Quality Control in LSR Molding Manufacturing
Quality control ensures product consistency and compliance with industry standards.
Key Inspection Methods:
- Dimensional measurement
- Visual inspection for flash or bubbles
- Shore hardness testing
- Tensile and tear strength testing
For medical LSR manufacturing, additional controls include:
- Cleanroom production
- Lot traceability
- Biocompatibility validation
7. Advantages of LSR Molding Manufacturing
LSR molding offers significant advantages over traditional rubber processes.
Key Benefits:
- Fully automated production
- High repeatability
- Minimal material waste
- Excellent surface finish
- No secondary curing required
Compared with compression , LSR manufacturing delivers higher efficiency and lower long-term costs.
9. Applications of LSR Molding Manufacturing
LSR molding is widely used across multiple industries.
Medical Industry
- Seals and diaphragms
- Catheters and valves
- Wearable medical devices
Automotive Industry
- Connector seals
- Sensor protection
- Gaskets and dampers
Consumer Products
- Baby care items
- Kitchenware
- Wearable electronics
Electronics Industry
- Waterproof components
- Keypads
- Insulation parts

11. Cost Considerations in LSR Molding Manufacturing
Key cost factors include:
- Mold tooling investment
- Material grade selection
- Production volume
- Automation level
While tooling costs are higher initially, LSR molding offers lower per-part costs in medium to high-volume production.
12. Best Practices for Successful LSR Molding Manufacturing
- Use experienced LSR mold designers
- Maintain clean material handling
- Optimize venting and gate design
- Implement strict process control
- Partner with an experienced LSR manufacturer
13. Conclusion
Understanding how to do LSR molding manufacturing is essential for producing high-quality liquid silicone rubber components. From material preparation and mold design to injection, curing, and quality control, every step plays a crucial role in achieving consistent and reliable results.

With the right equipment, tooling, and expertise, LSR molding manufacturing delivers superior performance, efficiency, and scalability for modern industrial applications.