Table of Contents
ToggleLiquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) molded components are used in medical devices, automotive systems, electronics, industrial seals, and consumer products due to their outstanding flexibility, durability, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility.
But how exactly are LSR molded components manufactured?

1. What Are LSR Molded Components?
LSR molded components are parts manufactured using Liquid Silicone Rubber injection molding technology. Unlike solid silicone rubber (HTV), LSR is a two-part, platinum-cured elastomer supplied in liquid form and processed in a closed injection molding system.
Key Characteristics of LSR Molded Parts
- High elasticity and tear resistance
- Excellent temperature resistance (-60°C to 200°C)
- Chemical and UV stability
- Biocompatibility and sterilization compatibility
- Precision molding with tight tolerances
These properties make LSR ideal for high-performance and regulated industries.
2. Common Applications of LSR Molded Components
LSR molding is widely used across multiple industries:
Medical & Healthcare
- Respirator masks and seals
- Catheter components
- Medical valves and diaphragms
- Wearable medical device housings
Automotive
- Connector seals
- Gaskets and O-rings
- Sensor protection covers
Electronics
- Waterproof seals
- Keypads
- Insulation components
Consumer & Industrial Products
- Baby care products
- Kitchenware
- Precision rubber components

3. Materials Used in LSR Molding
3.1 Composition of Liquid Silicone Rubber
LSR consists of:
- Part A: Silicone polymer + platinum catalyst
- Part B: Crosslinker + inhibitor
When mixed in a 1:1 ratio, the material cures under heat to form a solid elastomer.
3.2 Selecting the Right LSR Material
Key factors when choosing LSR:
- Shore hardness (typically 10A–80A)
- Transparency or color requirements
- Medical-grade or food-grade compliance
- Resistance to chemicals, oils, or steam
For regulated industries, USP Class VI, ISO 10993, FDA, or LFGB-certified LSR materials are often required.

4. LSR Mold Design: The Foundation of Quality
A well-designed mold is critical to producing high-quality LSR molded components.
4.1 Key Features of LSR Injection Molds
- Cold runner system to minimize material waste
- High-polish cavities for smooth surfaces
- Precision venting for air release
- Thermal insulation between hot and cold zones
4.2 Mold Materials
- Hardened stainless steel (S136)
- Corrosion-resistant materials for medical applications
4.3 Mold Design Considerations
- Uniform wall thickness
- Proper gate location
- Parting line optimization
- Flash control
Professional mold design ensures:
- Minimal flash
- Stable molding process
- Long mold life
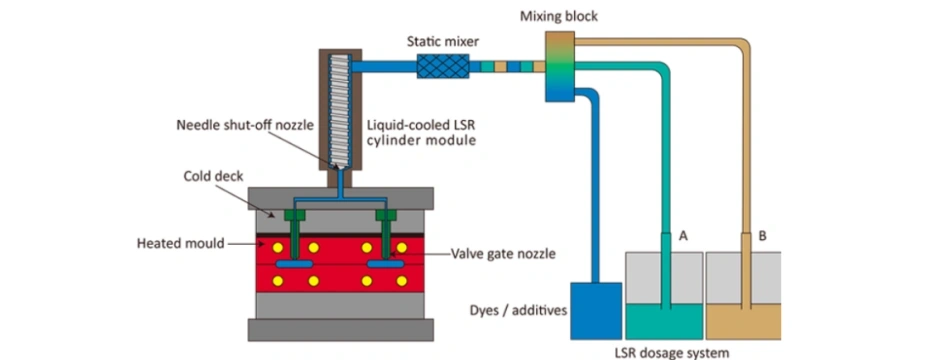
5. The LSR Injection Molding Process Explained
Step 1: Material Feeding and Mixing
LSR Part A and Part B are stored in sealed drums and pumped into a static mixer, ensuring precise 1:1 mixing without contamination.
Step 2: Injection into the Mold
The mixed LSR is injected into a closed, heated mold cavity using a specialized LSR injection molding machine.
Key parameters:
- Injection pressure
- Injection speed
- Mold temperature (typically 160–200°C)
Step 3: Curing and Crosslinking
Unlike thermoplastics, LSR cures through heat, forming a solid elastic component inside the mold.
Curing time:
- Usually 30 seconds to 2 minutes
- Depends on part thickness and material grade
Step 4: Demolding
LSR parts are flexible, allowing for:
- Automatic demolding
- Manual demolding for complex geometries
6. Post-Processing of LSR Molded Components
After molding, LSR components may require additional steps:
6.1 Deflashing
- Cryogenic deflashing
- Manual trimming
- Precision mold design can reduce or eliminate this step
6.2 Secondary Operations
- Overmolding with plastic or metal
- Laser marking
- Printing or coating
6.3 Post-Curing (If Required)
Some applications require post-curing to:
- Remove volatile residues
- Improve mechanical properties
7. Quality Control in LSR Molding
High-quality LSR molded components require strict quality control at every stage.
7.1 Incoming Material Inspection
- Certification verification
- Batch traceability
7.2 In-Process Monitoring
- Injection pressure and temperature tracking
- Visual inspection for flash, bubbles, or short shots
7.3 Final Inspection
- Dimensional measurement (CMM, optical inspection)
- Tensile strength and elongation testing
- Compression set testing
For medical and automotive parts, PPAP, IQ/OQ/PQ, and full traceability systems are commonly implemented.

8. Advantages of LSR Injection Molding
LSR molding offers several advantages over traditional rubber processing:
- High repeatability and automation
- Minimal material waste
- Excellent surface finish
- Tight dimensional tolerances
- Suitable for high-volume production
These benefits make LSR molding ideal for complex, high-precision rubber components.
9. Challenges in Making LSR Molded Components
Despite its advantages, LSR molding presents technical challenges:
- Flash control
- Tooling cost
- Strict process control
- Specialized equipment requirements
Working with an experienced LSR molding manufacturer helps overcome these challenges efficiently.
10. How to Choose the Right LSR Molding Manufacturer
When selecting a supplier for LSR molded components, consider:
- Experience with LSR injection molding
- In-house mold design and tooling
- Cleanroom or medical-grade production capability
- Certifications (ISO 13485, ISO 9001)
- Engineering support and DFM analysis
A reliable partner can help optimize design, reduce costs, and ensure consistent quality.

11. Future Trends in LSR Molded Components
The demand for LSR components continues to grow due to:
- Increasing medical device innovation
- Electrification in automotive systems
- Miniaturization of electronic devices
Emerging trends include:
- Multi-shot LSR overmolding
- Automated demolding systems
- Smart manufacturing and digital process control
Conclusion
Understanding how to make LSR molded components is essential for OEMs, engineers, and sourcing professionals looking for high-performance rubber solutions.
From material selection and mold design to precision injection molding and quality control, every step plays a critical role in producing reliable, durable, and compliant LSR parts.

By partnering with an experienced Liquid Silicone Rubber injection molding manufacturer, you can achieve consistent quality, cost efficiency, and long-term product success.