Table of Contents
ToggleIn the vast world of manufacturing and product design, the choice of material is paramount. It dictates everything from functionality and safety to cost and market perception. Two of the most common materials encountered are plastic and liquid silicone rubber (LSR). While both are polymers, their properties, applications, and performance are worlds apart.
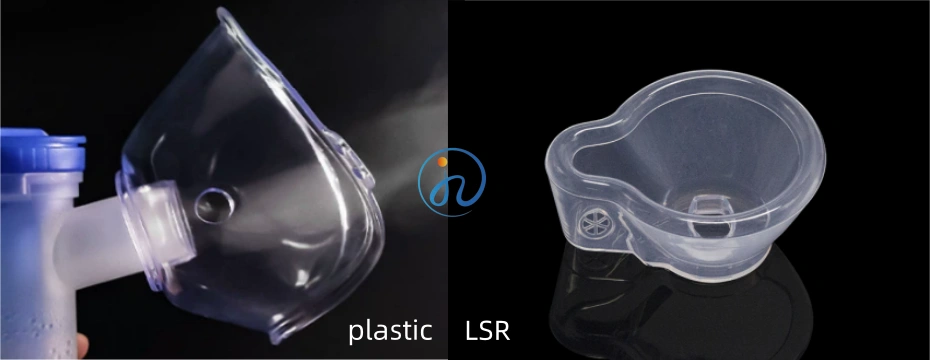
For professionals researching silicone products, understanding this distinction is crucial. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the battle of plastic products vs liquid silicone rubber products, empowering you to make the most informed decision for your next project.
Understanding the Basics: A Tale of Two Polymers
What are Plastic Products?
“Plastic” is a broad term for a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their versatility comes from their ability to be molded into solid objects of diverse shapes. Common types include:
- Thermoplastics: These soften when heated and harden when cooled (e.g., Polypropylene (PP), ABS, Nylon). They are recyclable.
- Thermosets: These undergo a chemical change when heated, creating a permanent solid shape that cannot be remelted (e.g., Epoxy, Polyurethane).
Plastics are typically injection-molded using pellets that are melted and forced into a mold cavity.
What are Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Products?
Liquid Silicone Rubber is a high-purity, two-part platinum-cured elastomer. It is supplied as a liquid and undergoes a thermoset curing process. Unlike plastics, LSR cures with heat into its elastic, rubber-like solid form. This process creates unique inherent properties that define high-performance silicone products.

Head-to-Head Comparison: Key Factors
To truly grasp which material is right for your application, we must break down their characteristics across several critical dimensions.
1. Temperature Resistance
- Plastic: Performance varies widely. Standard plastics like PP or ABS typically have a maximum continuous use temperature around 80-100°C (176-212°F). High-temperature engineering plastics (e.g., PEEK) can exceed 250°C (482°F) but are extremely expensive.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber: excels in this area. Standard LSR formulations comfortably operate in a range from -50°C to +200°C (-58°F to +392°F) continuously, with some specialty grades handling up to 300°C (572°F) for short periods. This makes silicone products ideal for applications like automotive under-the-hood components, kitchenware, and medical sterilization.
Winner: LSR for its consistent and wide operating temperature range.
2. Flexibility and Tactile Feel
- Plastic: Rigid by nature. While flexible variants exist (like certain TPEs), they are often proprietary blends. The feel of plastic is generally hard and unyielding.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber: Inherently flexible and elastic. It offers excellent compression set, meaning it returns to its original shape after deformation. The tactile feel is soft, smooth, and often described as “premium,” which is why it’s favored for consumer product grips, wearable devices, and baby products.
Winner: LSR for its superior elasticity and user-friendly tactile properties.
3. Biocompatibility and Safety
- Plastic: Not inherently biocompatible. Many plastics contain additives like plasticizers (e.g., BPA, phthalates) that can leach out, especially when heated. Achieving medical-grade status requires specific, often costly, formulations and rigorous testing.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber: Is naturally inert and hypoallergenic. Its platinum-cure process creates a pure material that is free of harmful by-products. It is naturally odorless and tasteless. FDA-approved, USP Class VI, and ISO 10993 compliant grades are readily available, making it the gold standard for medical silicone products like implants, seals for drug delivery devices, and baby bottle nipples.
Winner: LSR for its innate safety, purity, and ease of achieving medical certifications.
4. Durability and Lifespan
- Plastic: Susceptible to UV degradation, becoming brittle and discolored over time when exposed to sunlight. It can also be prone to stress cracking and has poor resistance to many chemicals.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber: Extremely durable against environmental factors. It boasts excellent resistance to UV light, ozone, and weathering. Its chemical resistance is strong against water, alcohols, and oxidizing agents, though it can be weakened by solvents and acids.
Winner: LSR for its exceptional weatherability and long-term stability.
5. Cost and Manufacturing
- Plastic: Generally wins on raw material cost per kilogram. The injection molding process for thermoplastics is also highly optimized and incredibly fast, leading to low per-part costs for high-volume production. The initial tooling cost can be lower for simpler parts.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber: The raw material cost is higher. The LSR injection molding process uses more complex machinery with two-part mixing and cold-runner systems to avoid curing in the feed lines. While cycle times can be competitive, the overall per-part cost is often higher. However, this must be weighed against the value of the superior properties it delivers.
Winner: Plastic for pure upfront and per-part cost in high volumes for non-demanding applications.

Application Spotlight: Where Each Material Shines
Ideal Uses for Plastic Products:
- Consumer Packaging: Bottles, containers, caps.
- Disposable Items: Cutlery, cups, razors.
- Structural Components: Housings for electronics, automotive interior trim, toys.
- Low-Cost Consumer Goods: Items where cost is the primary driver and high performance is not required.
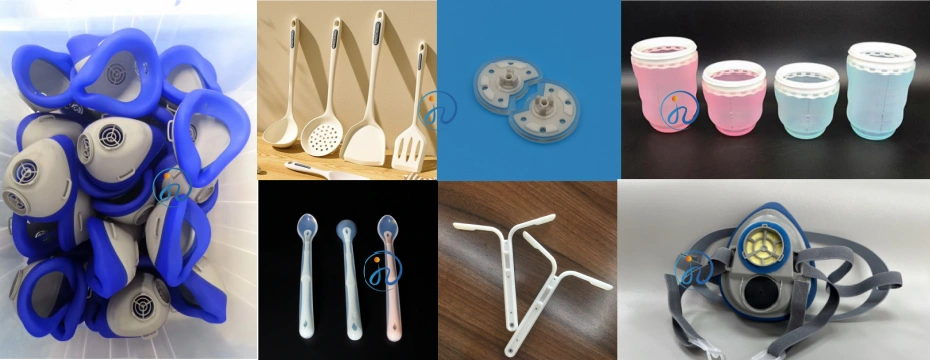
Ideal Uses for Liquid Silicone Rubber Products:
- Medical & Healthcare: Respiratory masks, seals for syringes, catheter components, wound care dressings, grommets.
- Baby & Childcare: Bottle nipples, pacifiers, teethers, watch straps.
- Automotive: Seals and gaskets for engines and transmissions, ignition cables, protective boots.
- Consumer Electronics: Waterproof seals for devices, keypads, tactile buttons, drone gaskets.
- Food & Beverage: Baking mats, spatulas, seals for appliances, ice cube trays.
- Aerospace: Seals and components requiring extreme temperature stability.
Making the Right Choice: A Summary
The decision between plastic and LSR isn’t about finding a “better” material, but the right material for the job.
Choose Plastic When:
- Your budget is the primary constraint.
- You need a rigid, structural part.
- The application has no extreme temperature, safety, or durability requirements.
- You anticipate very high production volumes where minor cost savings multiply.
Choose Liquid Silicone Rubber (Prioritizing Silicone Products) When:
- Safety and biocompatibility are non-negotiable (medical, food, baby).
- Your product will face extreme temperatures, either high or low.
- You require flexibility, elasticity, and a soft-touch feel.
- Long-term durability and resistance to weathering are critical.
- The perceived value and premium quality of the material justify a higher cost.
Conclusion: The Value Proposition of Silicone Products
While plastic remains the undisputed king of high-volume, low-cost manufacturing, Liquid Silicone Rubber has carved out an essential niche as a high-performance elastomer. The evolution of silicone products represents a shift in market demand towards materials that offer not just functionality, but also safety, durability, and a superior user experience.

For engineers, designers, and product managers, the key is to look beyond the simple per-part cost. By considering the total value—including reduced failure rates, regulatory compliance, brand enhancement, and end-user satisfaction—the investment in high-quality silicone products often proves to be the most intelligent and profitable choice in the long run.
When your project’s requirements demand the best in class for safety, performance, and reliability, the answer is clear: Liquid Silicone Rubber is the material that delivers.