Table of Contents
ToggleLiquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection molding is used in industries that require high precision, durability, and cleanliness, such as medical devices, automotive components, and consumer electronics.
When discussing LSR tooling systems, most people are familiar with cold runner LSR molds, but fewer truly understand what a hot runner LSR mold is, how it works, and when it should be used.
So, what is a hot runner LSR mold, and how does it differ from conventional runner systems?
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive explanation of hot runner LSR molds, including their structure, working principles, advantages, limitations, applications, and a detailed comparison with cold runner systems.

What Is a Hot Runner LSR Mold?
A hot runner LSR mold is a type of injection mold used for Liquid Silicone Rubber processing in which the runner system is heated or thermally managed to keep the silicone material in a fluid or semi-reactive state until it enters the mold cavity.
Unlike thermoplastic hot runner systems, LSR hot runner molds must carefully balance temperature to avoid premature curing while ensuring smooth flow and consistent injection.
Because LSR is a thermosetting elastomer, hot runner designs for silicone are significantly more complex than those used in plastic injection molding.
How Does a Hot Runner LSR Mold Work?
To understand the function of a mold, it’s essential to understand the curing behavior of LSR.
Basic Working Principle
- Material Preparation
Two-component LSR (Part A and Part B) is mixed in a precise ratio and injected into the molding system. - Hot Runner Manifold
The runner system is thermally controlled to maintain optimal flow without triggering early vulcanization. - Direct Gating into Cavities
LSR is injected directly into the cavities through open or valve gates. - Cavity Heating and Curing
Mold cavities are heated to initiate cross-linking and curing. - Demolding
Once cured, the finished silicone parts are demolded manually or automatically.
This design aims to reduce runner waste and improve production efficiency, though it requires advanced temperature control.
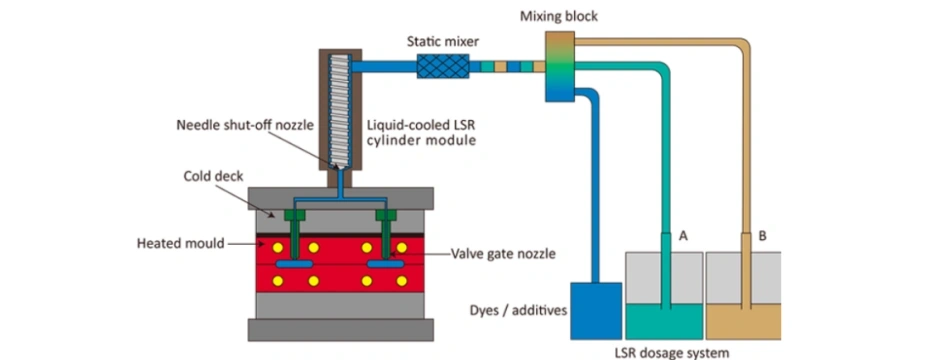
Key Components of a Hot Runner LSR Mold
A well-designed injection mold includes several precision components:
1. Hot Runner Manifold
- Thermally regulated channels
- Maintains stable material flow
- Requires precise insulation
2. Heating System
- Cartridge heaters or heating plates
- Accurate temperature sensors (thermocouples)
3. Gate System
- Open gate design (most common)
- Valve gate systems for high-precision parts
4. Mold Cavities
- Heated steel cavities for curing
- High-polish surface finishes
5. Temperature Control Unit (TCU)
- Independent temperature zones
- Critical for process stability
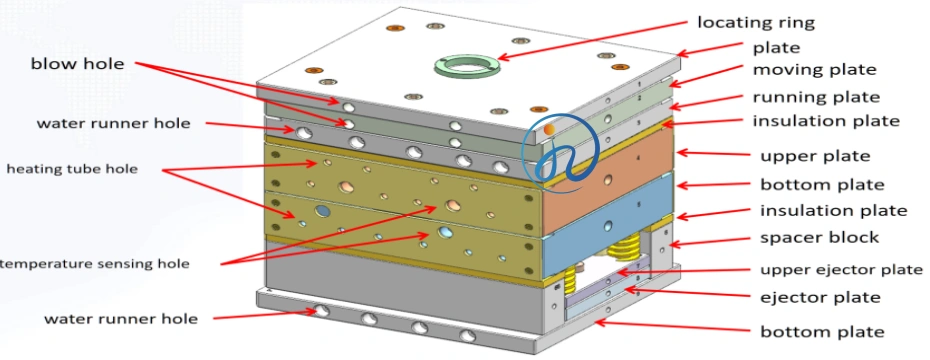
Advantages of Hot Runner LSR Mold
Although less common than cold runner systems, hot runner LSR molds offer several notable benefits in specific applications.
1. Reduced Material Waste
Hot runner systems can significantly reduce or eliminate runner waste, improving material utilization.
2. Faster Cycle Times
Direct injection and optimized flow paths can reduce cycle time in certain production scenarios.
3. Improved Mold Filling Balance
Well-designed hot runner manifolds ensure even material distribution across multi-cavity molds.
4. Compact Mold Design
Without cold runner plates, molds can be more compact and space-efficient.
5. Suitable for Certain High-Volume Parts
For specific geometries and production volumes, hot runner LSR molds can offer cost advantages.
Limitations and Challenges of Hot Runner LSR Mold
Despite their advantages, hot runner LSR molds also present technical challenges.
1. Risk of Premature Curing
LSR cures when exposed to heat, making temperature control extremely critical. Any imbalance may cause curing inside the runner.
2. Complex Temperature Management
Multiple heating zones must be precisely controlled, increasing system complexity.
3. Higher Maintenance Requirements
Hot runner systems require regular cleaning, inspection, and maintenance.
4. Higher Tooling Cost
Initial mold and system costs are generally higher than cold runner molds.
5. Limited Application Range
Hot runner LSR molds are not suitable for all part designs or materials.
Typical Applications of Hot Runner LSR Mold
Although niche, hot runner LSR molds are used in certain industries:
Automotive Industry
- Sealing components
- Vibration dampers
- High-volume standardized parts
Industrial Components
- Simple geometry silicone parts
- Large-volume production with stable designs
Consumer Products
- Standardized silicone accessories
- Non-cosmetic critical surfaces

Design Considerations for Hot Runner LSR Mold
Proper design is essential for successful hot runner LSR molding.
1. Accurate Thermal Insulation
Prevents heat transfer to unwanted areas.
2. Flow Path Optimization
Short, balanced runner paths reduce residence time.
3. Gate Design Selection
Valve gates improve surface quality but increase complexity.
4. Mold Steel Selection
- S136
- Stainless steel for medical-grade requirements
5. Process Monitoring
Real-time temperature and pressure monitoring is recommended.
Future Trends in Hot Runner LSR Mold Technology
- Advanced thermal insulation materials
- Improved valve gate technology
- Smart temperature control systems
- Hybrid hot-cold runner solutions
- Increased automation and monitoring

Conclusion
It is a specialized injection molding solution designed to reduce material waste and improve efficiency in certain Liquid Silicone Rubber applications. While technically complex and less commonly used than cold runner systems, hot runner LSR molds can be effective when carefully designed and properly controlled.
Choosing between a hot runner LSR mold and a cold runner LSR mold depends on part geometry, production volume, material behavior, and cost considerations. For most LSR applications, cold runner systems remain the industry standard, but hot runner molds still play a role in niche, high-volume scenarios.