Table of Contents
ToggleInjection molding of parts using liquid silicone rubber (LSR) is a highly precise manufacturing process used to produce flexible, durable, and high-purity silicone components. Due to its excellent material properties, LSR injection molding is widely adopted in industries such as medical devices, automotive, electronics, consumer products, and infant care.
Compared with traditional rubber molding methods, LSR injection molding offers higher consistency, automation, and production efficiency, making it ideal for both low- and high-volume manufacturing.

2. What Is Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)?
Liquid Silicone Rubber is a two-component, platinum-cured elastomer supplied in liquid form. It consists of:
- Part A: Silicone polymer with catalyst
- Part B: Silicone polymer with cross-linker
The two components are mixed in a 1:1 ratio during molding and cured by heat inside a closed mold.
Key Characteristics of LSR:
- Excellent elasticity and flexibility
- High thermal stability
- Chemical and UV resistance
- Biocompatibility (medical grades)
- Long service life
These properties make LSR ideal for precision molded parts.
3. What Is LSR Injection Molding?
Liquid silicone rubber injection molding is a closed-loop manufacturing process where mixed LSR material is injected into a heated mold cavity, vulcanized, and formed into a finished silicone part.
Unlike thermoplastics, LSR does not melt and re-solidify. Instead, it cures through a chemical reaction, forming a stable elastic structure.

4. How the Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding Process Works
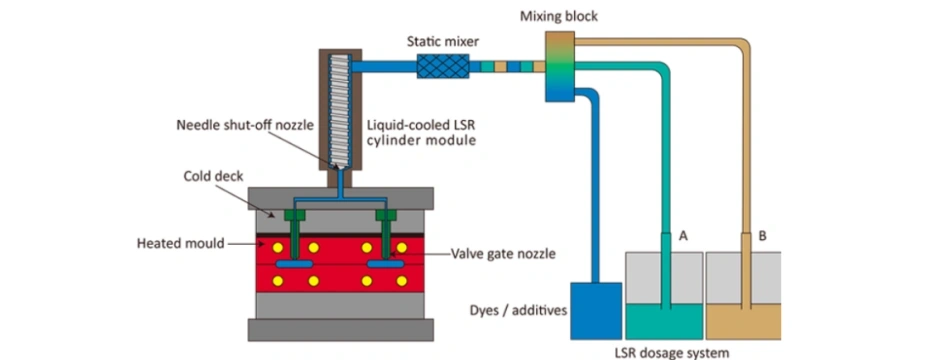
4.1 Material Dosing and Mixing
LSR components A and B are stored in sealed containers and pumped into a static mixer at an exact 1:1 ratio. Pigments or additives may be added at this stage.
4.2 Injection into the Mold
The mixed LSR is injected under low pressure into a heated mold cavity, typically using a cold runner system to prevent premature curing.
4.3 Vulcanization (Curing)
Inside the mold, LSR cures rapidly at temperatures between 160°C and 200°C, forming the final elastomeric part.
4.4 Demolding
Once cured, the silicone part is demolded automatically or manually, depending on part complexity.
5. Types of Parts Produced by LSR Injection Molding
Injection molding of parts using liquid silicone rubber is suitable for:
- Seals and O-rings
- Gaskets and diaphragms
- Keypads and buttons
- Medical device components
- Baby care products
- Electrical insulation parts
LSR is especially suitable for thin-wall, complex, and high-precision parts.
6. Advantages of Injection Molding Parts Using Liquid Silicone Rubber
6.1 High Precision and Consistency
LSR injection molding achieves tight tolerances and repeatable part quality, ideal for medical and technical applications.
6.2 Automated Production
The process is highly automated, reducing labor costs and human error.
6.3 Flash-Free Molding
With proper mold design, LSR molding produces minimal or no flash, reducing secondary operations.
6.4 Excellent Material Performance
LSR molded parts offer:
- Superior elasticity
- Low compression set
- Resistance to heat, aging, and chemicals
6.5 Clean and Contamination-Free
LSR molding can be performed in cleanroom environments, essential for medical and food-contact products.
7. Mold Design for Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
7.1 Cold Runner Systems
Most LSR molds use cold runner systems to keep material uncured before injection, minimizing waste.
7.2 Venting Design
Proper venting allows trapped air to escape, preventing defects and bubbles.
7.3 Steel Selection
High-quality stainless steel ensures durability, corrosion resistance, and cleanroom compatibility.
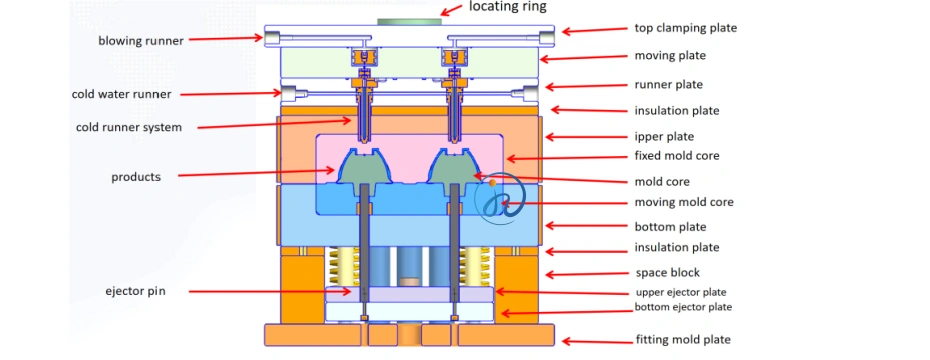
8. Design Considerations for LSR Injection Molded Parts
Key design factors include:
- Uniform wall thickness
- Proper draft angles
- Avoiding sharp corners
- Gate location optimization
- Parting line control
Designing for LSR differs from thermoplastics and requires specialized expertise.
9. Secondary Processes After LSR Injection Molding
9.1 Deflashing
Minimal flash may be removed using:
- Cryogenic deflashing
- Manual trimming
9.2 Post-Curing
Some applications require post-curing to improve mechanical properties or remove volatile compounds.
10. Quality Control in LSR Injection Molding
Quality inspection typically includes:
- Dimensional measurement
- Visual inspection
- Tensile and elongation testing
- Compression set testing
- Material traceability
For medical applications, biocompatibility and cleanliness testing are also required.

11. Applications of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molded Parts
Medical Industry
- Seals and valves
- Respiratory components
- Drug delivery parts
Automotive Industry
- Connector seals
- Sensor covers
- Gaskets
Consumer Products
- Wearables
- Baby care products
- Kitchenware
Electronics
- Insulation components
- Waterproof seals

12. How to Choose the Right LSR Injection Molding Partner
When selecting an LSR molding supplier, consider:
- Experience with liquid silicone rubber
- In-house mold design capability
- Cleanroom production options
- Quality certifications
- Engineering support
A reliable partner helps reduce risk and shorten product development cycles.
13. Conclusion
Injection molding of parts using liquid silicone rubber is a high-precision, efficient, and reliable manufacturing process for producing advanced silicone components. With its excellent material properties and compatibility with automated production, LSR injection molding is the preferred solution for demanding applications across multiple industries.

By understanding the process and choosing the right manufacturing partner, companies can achieve consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and long-term product performance.