Table of Contents
ToggleLiquid Silicone Rubber injection molding has become one of the most important manufacturing processes for high-precision silicone parts used in medical, automotive, electronics, and consumer products. At the core of this process lies a critical tool: the LSR injection molding mold.
So, what exactly is an LSR injection molding mold? How does it work, and why is it different from traditional plastic injection molds? This article provides a complete, in-depth guide to help buyers and engineers understand LSR molds, their structure, types, advantages, and design considerations.

1. What Is an LSR Injection Molding Mold?
An LSR injection molding mold is a precision-engineered tool specifically designed to process liquid silicone rubber, a two-part platinum-cured elastomer, into finished parts under controlled temperature and pressure.
Unlike thermoplastic molds, LSR molds are built to handle:
- Low-viscosity liquid materials
- Cold-runner feeding systems
- High-temperature curing inside the mold
- Tight tolerances and flash-free requirements
The mold shapes and cures the LSR material by injecting it into heated cavities, where it crosslinks and solidifies into elastic silicone components.
2. How LSR Injection Molding Mold Works
The working principle of an LSR injection molding mold differs significantly from conventional plastic molding.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Material Preparation
LSR consists of Part A and Part B, which are stored separately and mixed in a precise 1:1 ratio. - Cold Runner Feeding
The mixed LSR is injected through a cold runner system, keeping the material uncured before entering the cavity. - Injection into Heated Mold
The mold cavities are heated (typically 160–200°C), triggering rapid curing once the LSR enters. - Curing & Crosslinking
LSR vulcanizes inside the cavity instead of cooling like plastic. - Demolding
The flexible silicone part is ejected, often without ejector pins, thanks to its elasticity.
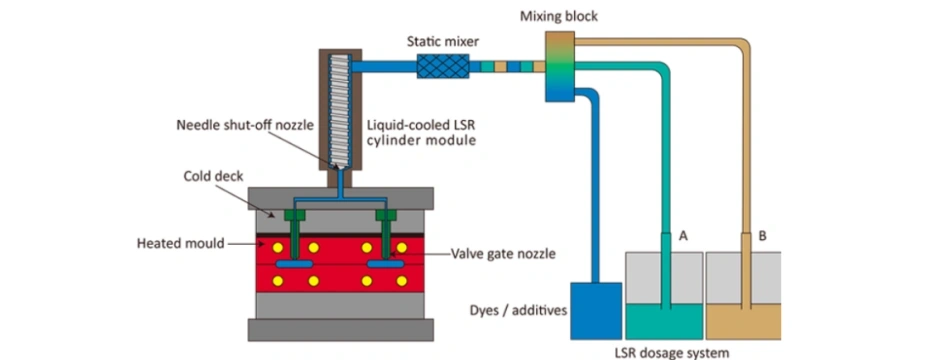
3. Key Components of an LSR Injection Molding Mold
An LSR mold is more complex than standard injection molds. Its main components include:
Mold Cavities
- Precision-machined to ensure dimensional accuracy
- Designed to minimize flash
Cold Runner System
- Maintains LSR in liquid state
- Reduces material waste
- Enables fully automated production
Heating System
- Cartridge heaters or heating plates
- Uniform temperature control is critical
Venting System
- Micro-vents allow trapped air to escape
- Essential for bubble-free parts
Mold Surface Treatment
- Polished or coated to improve demolding
- Reduces sticking and contamination
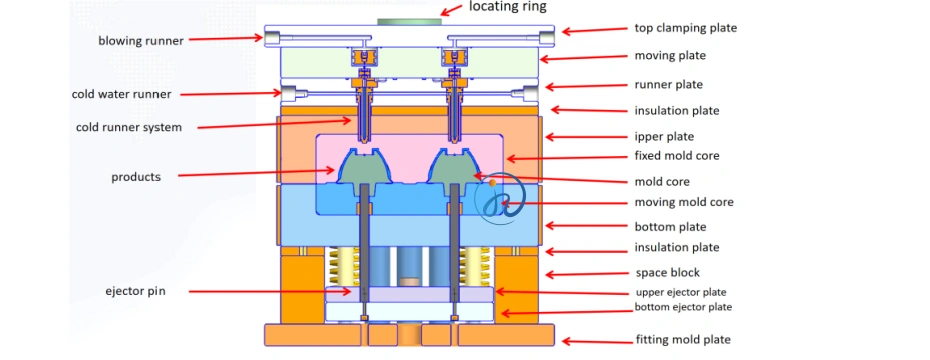
4. Types of LSR Injection Molding Molds
Depending on product design, volume, and budget, LSR molds can be classified into several types.
4.1 Cold Runner LSR Mold
This is the most commonly used type.
Advantages:
- Minimal material waste
- Stable process
- Suitable for high-volume production
Applications:
- Medical seals
- Baby care products
- Electronic gaskets
4.2 Hot Runner LSR Mold
Hot runner systems are less common in LSR but used in specific applications.
Advantages:
- Faster cycle time
- Precise gating control
Limitations:
- Higher mold cost
- Complex temperature control
4.3 Multi-Cavity LSR Mold
Designed to increase production efficiency.
Features:
- 4, 8, 16, or more cavities
- Balanced runner design
- Consistent part quality
4.4 Overmolding LSR Mold
Used to bond silicone directly onto plastic or metal substrates.
Common combinations:
- LSR + PC
- LSR + PA
- LSR + Stainless Steel

5. Materials Used for LSR Injection Molding Molds
Choosing the right mold steel is critical for durability and product quality.
Common Mold Materials:
- H13 Steel – High temperature resistance
- S136 Stainless Steel – Corrosion-resistant, medical-grade applications
- NAK80 – Excellent polishability
For medical and food-grade LSR parts, stainless steel molds are often required to meet hygiene standards.
6. Design Considerations for LSR Injection Molding Mold
Proper mold design determines success or failure in LSR molding.
6.1 Flash Control
LSR flows easily, so mold parting lines must be extremely precise. Typical tolerances are within ±0.005 mm.
6.2 Venting Design
Insufficient venting leads to:
- Air traps
- Short shots
- Surface defects
Micro-vent depth usually ranges from 0.003–0.01 mm.
6.3 Gate Design
Common gate types:
- Valve gates
- Pin-point gates
- Submarine gates
Gate location impacts flow balance and cosmetic appearance.
6.4 Demolding Strategy
Because LSR parts are flexible:
- Draft angles can be minimal
- Ejector pins may not be required
7. Advantages of LSR Injection Molding Mold
LSR molds enable manufacturers to produce high-performance silicone parts with unique benefits.
Key Advantages:
- High precision and repeatability
- Fully automated production
- No post-curing required
- Excellent surface finish
- Long mold life
Compared with compression molding, LSR injection molding delivers higher efficiency and lower labor costs.
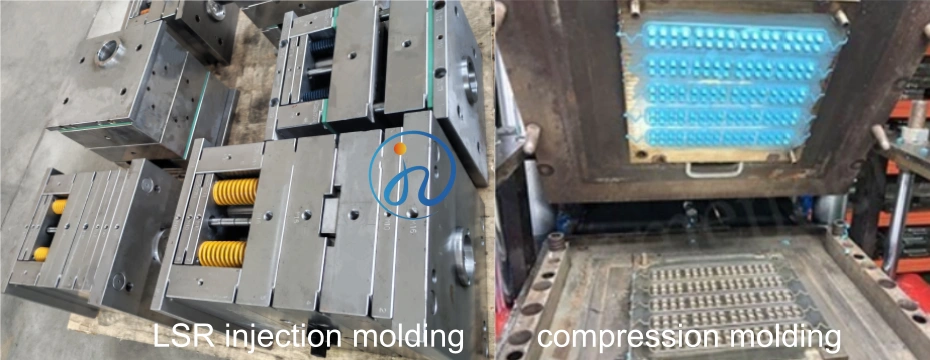
8. Applications of LSR Injection Molding Molds
LSR molds are widely used across multiple industries.
Medical Industry
- Seals and diaphragms
- Catheter components
- Respiratory masks
Automotive Industry
- Connector seals
- Sensor covers
- Vibration dampers
Consumer Products
- Baby bottle nipples
- Wearable device straps
- Kitchenware
Electronics
- Waterproof gaskets
- Keypads
- Insulation components

9. Cost of LSR Injection Molding Mold
The cost of an LSR mold depends on several factors:
- Number of cavities
- Mold steel material
- Runner system type
- Part complexity
- Surface finish requirements
Typical cost range:
USD 8,000 – 60,000+, depending on complexity.
While the initial cost is higher than traditional molds, long-term production savings often justify the investment.
10. How to Choose the Right LSR Injection Molding Mold Supplier
When sourcing LSR molds, look for suppliers with:
- In-house mold design and manufacturing
- Experience in LSR processing
- Medical or food-grade certifications
- Automated cold runner systems
- Proven quality control
A reliable supplier ensures mold longevity, stable production, and consistent part quality.

11. Conclusion
An LSR injection molding mold is the foundation of high-quality liquid silicone rubber production. Its specialized design, cold runner system, precision machining, and thermal control make it uniquely suited for manufacturing advanced silicone components.
Whether you are developing medical devices, automotive seals, or consumer products, understanding how LSR molds work helps you make better decisions on tooling investment, supplier selection, and product design.
If you are looking for a long-term, scalable solution for silicone part production, LSR injection molding molds offer unmatched performance and reliability.