Table of Contents
ToggleLSR silicone molded components are increasingly used in medical, automotive, electronics, and industrial applications due to their exceptional performance, precision, and reliability. But what exactly are LSR silicone molded components, and why are they becoming the preferred choice for high-end rubber parts?

1. What Is LSR Silicone?
LSR stands for Liquid Silicone Rubber, a two-part, platinum-cured elastomer supplied in liquid form. Unlike solid silicone rubber (HTV), LSR is processed using injection molding technology, enabling high-precision and fully automated production.
Basic Composition of LSR
- Part A: Silicone polymer with catalyst
- Part B: Crosslinker and additives
These two components are mixed in a 1:1 ratio and cured by heat inside a closed mold.
2. What Are LSR Silicone Molded Components?
LSR silicone molded components are finished parts produced by injecting liquid silicone rubber into a precision mold, where it cures and forms a flexible, durable elastomeric product.
- High dimensional accuracy
- Smooth surface finish
- Excellent mechanical consistency
- Ability to meet medical and food-grade standards

3. Key Properties of LSR Silicone Molded Components
LSR silicone molded parts offer a unique combination of properties that few other elastomers can match.
3.1 Mechanical Properties
- High elasticity and resilience
- Excellent tear and tensile strength
- Low compression set
3.2 Thermal Performance
- Operating temperature range: -60°C to +200°C
- Maintains flexibility in extreme temperatures
3.3 Chemical and Environmental Resistance
- Resistant to oils, chemicals, and solvents
- UV, ozone, and weather resistant
3.4 Biocompatibility
- Odorless and tasteless
- Suitable for medical-grade and food-grade applications
- Compatible with sterilization methods (steam, gamma, EtO)
4. How Are LSR Silicone Molded Components Made?
Step 1: Material Preparation
LSR materials are stored in sealed containers to avoid contamination. Parts A and B are pumped into a static mixer to ensure precise blending.
Step 2: Injection Molding
The mixed LSR is injected into a heated mold cavity using an LSR injection molding machine. Unlike thermoplastics, LSR cures under heat instead of cooling.
Step 3: Curing Process
Inside the mold, the silicone crosslinks and solidifies within seconds to minutes, depending on part design and thickness.
Step 4: Demolding and Inspection
Once cured, the flexible LSR part is demolded automatically or manually and inspected for quality.
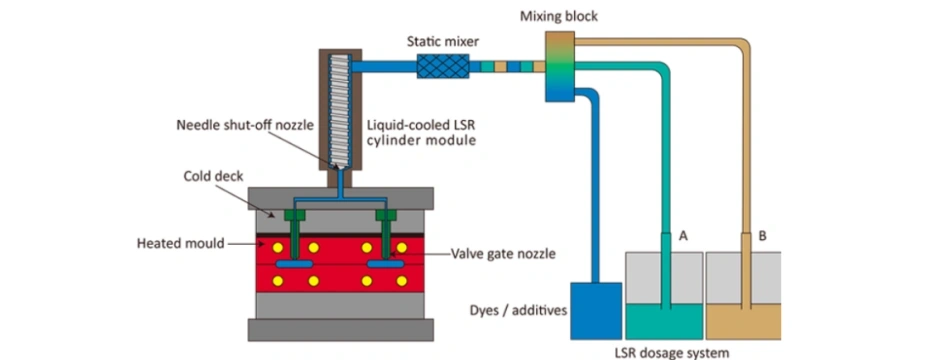
5. LSR Mold Design
Mold design plays a critical role in producing high-quality LSR molded components.
Key Features of LSR Molds
- Cold runner system to minimize material waste
- Precision venting to release trapped air
- High-polish cavities for smooth surfaces
- Tight tolerance control
Mold Materials
- Hardened steel (S136)
- Stainless steel for medical and cleanroom production
6. Types of LSR Silicone Molded Components
6.1 Standard LSR Molded Parts
- O-rings and gaskets
- Seals and diaphragms
6.2 LSR Overmolded Components
- Silicone bonded to plastic or metal
- Used in electronics and medical devices
6.3 Multi-Shot LSR Components
- Multi-material or multi-color parts
- Advanced functional designs
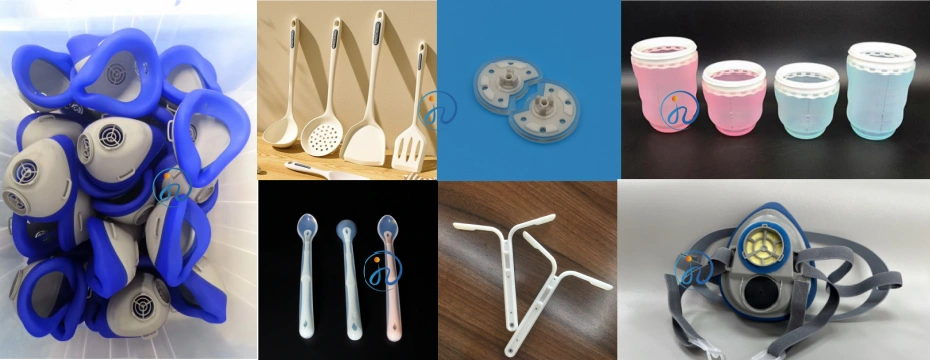
7. Applications
Medical & Healthcare
- Respirator and mask seals
- Catheters and valves
- Medical wearables
Automotive
- Connector seals
- Sensor covers
- Vibration dampers
Electronics
- Waterproof seals
- Silicone keypads
- Insulating components
Consumer & Industrial Products
- Baby care products
- Kitchenware components
- Precision industrial parts
8. Advantages
LSR molding offers several advantages over traditional rubber processing methods:
- High automation and consistency
- Minimal material waste
- Excellent surface quality
- Tight dimensional tolerances
- Suitable for mass production
9. LSR Silicone vs Other Rubber Molded Components
Liquid silicone rubber compare Solid Silicone Rubber (HTV)
- Faster cycle times
- Higher precision
- Less manual labor
LSR vs TPE or EPDM
- Better heat resistance
- Superior chemical stability
- Longer service life

10. Quality Standards
Depending on application, LSR parts may comply with:
- ISO 9001
- ISO 13485 (medical)
- FDA
- LFGB
- USP Class VI
Strict quality control ensures consistency, safety, and regulatory compliance.
11. Challenges in Producing
Despite its advantages, LSR molding requires:
- High initial tooling investment
- Advanced process control
- Experienced mold and process engineers
Choosing an experienced LSR manufacturer is essential to overcome these challenges.
12. How to Choose the Right LSR Silicone Molded Components Manufacturer
Key factors to evaluate:
- LSR injection molding experience
- In-house mold design and tooling
- Cleanroom or medical-grade capability
- Engineering and DFM support
- Stable quality control systems
A professional supplier can help optimize design, reduce cost, and ensure long-term reliability.

Conclusion
LSR silicone molded components are high-performance elastomer parts produced through advanced LSR injection molding technology. With their exceptional precision, durability, and compliance with strict industry standards, they have become the preferred solution for medical, automotive, and electronic applications.
Understanding what LSR silicone molded components are and how they are manufactured allows OEMs and buyers to make informed decisions and choose the right manufacturing partner for long-term success.