Table of Contents
ToggleLiquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection molding is a highly precise manufacturing process used in medical devices, automotive components, consumer electronics, baby products, and industrial sealing applications.
When discussing LSR injection molding projects, one term appears in almost every quotation, feasibility discussion, and production plan: tooling.
For many buyers and even some engineers, tooling is often misunderstood. Questions such as:
- What exactly is tooling in LSR injection molding?
- Why is tooling cost so high compared to plastic molds?
- How does tooling design affect part quality and production efficiency?
- Is tooling a one-time investment or a recurring cost?
This article provides a complete and practical explanation of tooling in LSR injection molding, helping you understand its structure, function, cost drivers, and importance in achieving high-quality LSR parts.
What Is Tooling in LSR Injection Molding?
Definition of Tooling in LSR Injection
Tooling in LSR injection molding refers to the precision-engineered mold system and related components used to shape, cure, and produce liquid silicone rubber parts.
Unlike conventional plastic injection tooling, LSR tooling must handle:
- Extremely low-viscosity material
- Precise metering and injection
- Controlled curing at high temperatures
- Zero or ultra-low flash requirements
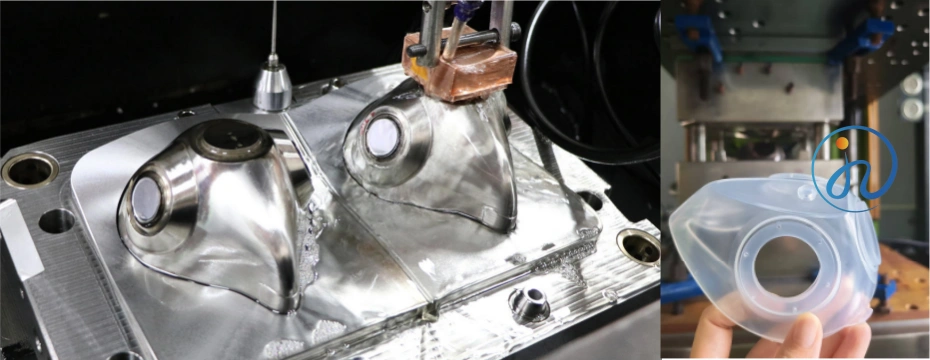
Why Tooling Is So Important in LSR Injection
LSR tooling directly determines:
- Part dimensional accuracy
- Surface finish quality
- Flash control
- Cycle time
- Material waste
- Production stability
Even with the better LSR injection machines, poor tooling design will result in defects, high scrap rates, and unstable mass production.
That is why tooling is often considered the most critical investment in an LSR project.
Key Components of LSR Injection Tooling
LSR tooling is more complex than standard thermoplastic molds. A typical LSR injection mold includes the following major components:
1. Mold Cavities and Cores
- Form the final shape of the LSR part
- Precision-machined with tight tolerances
- Often polished to a mirror finish
- Designed to minimize part adhesion
High-quality cavity design ensures:
- Accurate dimensions
- Consistent part weight
- Smooth surface finish
2. Cold Runner System
Unlike thermoplastics, LSR injection molding typically uses a cold runner system.
Its function is to:
- Keep LSR material uncured before injection
- Prevent premature cross-linking
- Reduce material waste
A well-designed cold runner system improves:
- Material efficiency
- Process stability
- Long-term production cost
3. Injection and Gating System
The injection system controls how LSR flows into the cavity.
Key considerations include:
- Balanced flow paths
- Gate size and location
- Minimizing air entrapment
Proper gating design prevents:
- Short shots
- Weld lines
- Incomplete filling
4. Venting System
Because LSR has very low viscosity, venting is critical.
The venting system:
- Allows trapped air to escape
- Prevents bubbles and voids
- Ensures complete cavity filling
Poor venting is one of the most common causes of defects in LSR parts.
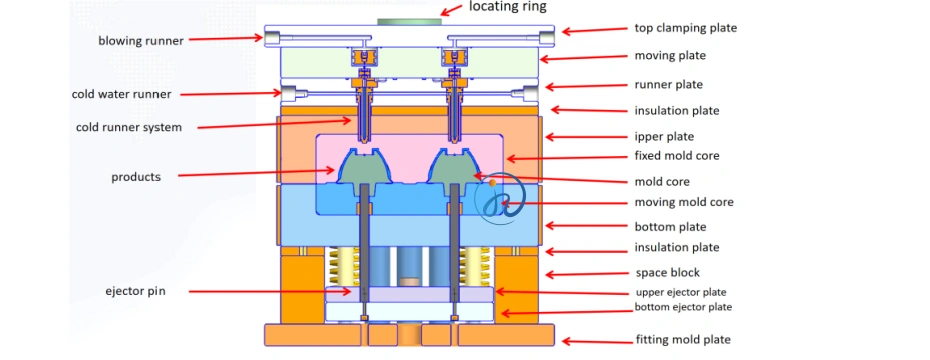
5. Heating and Temperature Control System
LSR tooling includes:
- Integrated heating elements
- Precise temperature control zones
The heating system ensures:
- Consistent curing
- Stable cycle times
- Uniform mechanical properties
6. Mold Base and Structural Components
The mold base supports:
- All tooling components
- Alignment and clamping stability
High-quality mold bases improve:
- Tooling lifespan
- Production repeatability
- Maintenance efficiency

Tooling Cost in LSR Injection Molding
Is Tooling a One-Time Cost?
Yes. In most LSR projects:
- Tooling is a one-time upfront investment
- Paid before mass production
- Used for long-term production
However, tooling maintenance and potential modifications may generate additional costs over time.
Factors That Affect LSR Tooling Cost
1. Part Design Complexity
- Thin walls
- Undercuts
- Micro features
- Tight tolerances
More complex designs require advanced machining and engineering.
2. Number of Cavities
- Single-cavity molds cost less initially
- Multi-cavity molds increase tooling cost but reduce unit price
3. Tool Steel and Material Selection
- Hardened steel for high-volume production
- Stainless steel for medical and food-grade applications
4. Cold Runner System Design
Advanced cold runner systems:
- Increase tooling cost
- Reduce long-term material waste
5. Surface Finish Requirements
- Polished, textured, or matte finishes
- Medical and consumer products often require higher standards
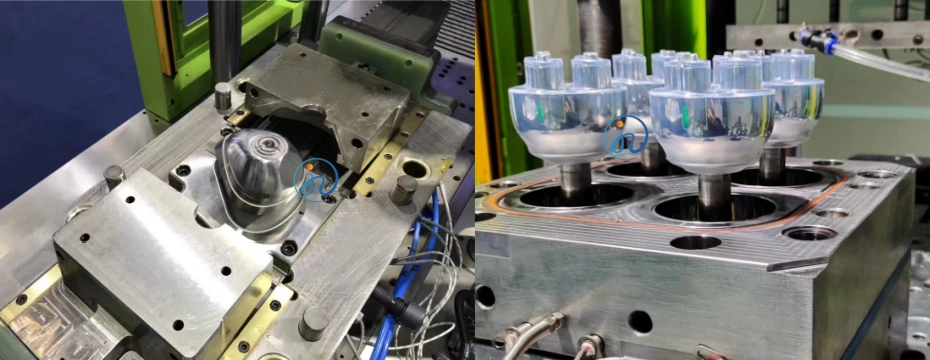
How Tooling Design Impacts LSR Part Quality
Tooling design directly affects:
1. Flash Control
LSR is extremely sensitive to parting line gaps.
Precision tooling minimizes flash and reduces post-processing.
2. Dimensional Stability
Well-designed tooling ensures:
- Consistent part size
- Minimal shrinkage variation
- Stable assembly performance
3. Surface Appearance
Tool polishing and cavity finish determine:
- Smoothness
- Gloss level
- Cosmetic quality
4. Mechanical Performance
Uniform curing improves:
- Tensile strength
- Tear resistance
- Elastic recovery
Tooling Ownership and Responsibility
In most LSR injection molding projects:
- Tooling is paid for by the customer
- Tooling belongs to the customer
- Stored and maintained by the manufacturer
Clear tooling ownership terms should be included in:
- Quotation
- Manufacturing agreement
- NDA or tooling agreement
Tooling Validation and Testing
Before mass production, LSR tooling typically undergoes:
- Mold trial (T1, T2 samples)
- Dimensional inspection
- Material performance testing
- Process parameter optimization
This validation phase ensures:
- Tooling meets design intent
- Parts meet functional requirements
- Production is stable and repeatable

Common Tooling Mistakes in LSR Injection
1. Underestimating Tooling Importance
Focusing only on part price often leads to poor tooling decisions.
2. Ignoring DFM (Design for Manufacturability)
Early DFM feedback can significantly reduce tooling risk and cost.
3. Choosing the Lowest Tooling Quote
Low-cost tooling often results in:
- Short mold life
- High scrap rates
- Frequent repairs
How to Optimize Tooling for LSR Injection
For Engineers
- Design consistent wall thickness
- Avoid unnecessary sharp corners
- Allow proper venting locations
For Buyers
- Share accurate annual volume forecasts
- Define quality and tolerance requirements clearly
- Work with experienced LSR tooling suppliers
Why Experienced LSR Tooling Manufacturers Matter
An experienced LSR manufacturer offers:
- In-house tooling design and machining
- Proven cold runner technology
- Process optimization expertise
- Long-term production support
Choosing the right tooling partner helps:
- Reduce development risk
- Shorten time to market
- Lower total project cost
Conclusion
So, what is tooling in LSR injection molding?
Tooling is the core manufacturing system that enables liquid silicone rubber to be molded into precise, high-quality parts. It determines not only the shape of the product but also its quality, consistency, and production efficiency.

To summarize:
- Tooling is a one-time investment
- It includes cavities, runners, venting, and heating systems
- Tooling quality directly impacts part performance and cost
- Smart tooling decisions lead to long-term success in LSR projects
If you are planning an LSR injection molding project, investing in well-designed tooling and an experienced manufacturing partner is the key to reliable, scalable, and cost-effective production.