Table of Contents
ToggleThe overmolding LSR injection molding process is an advanced manufacturing technique where liquid silicone rubber (LSR) is molded directly over another substrate—such as plastic, metal, or electronic components—to create a single, integrated part.
This process combines the flexibility, biocompatibility, and durability of LSR with the structural strength of rigid materials, making it widely used in medical devices, automotive components, consumer electronics, and industrial products.
In this guide, we’ll explain how LSR overmolding works, its advantages, materials compatibility, applications, and design considerations—helping engineers and buyers decide whether it’s the right solution for their projects.
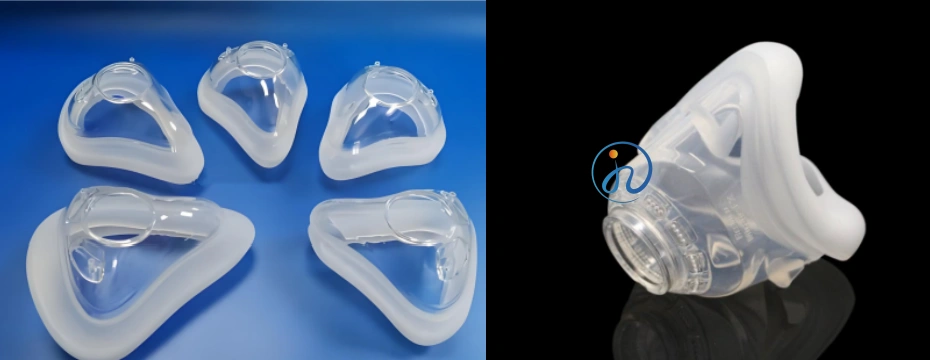
What Is LSR Overmolding?
LSR overmolding refers to a process where liquid silicone rubber is injection molded onto a pre-molded or pre-inserted component, forming a permanent bond without the need for adhesives.
Unlike traditional rubber molding, LSR overmolding:
- Uses two-part liquid silicone
- Is fully automated
- Produces high-precision, flash-free parts
- Is suitable for cleanroom and medical-grade manufacturing
The result is a multi-material component that combines soft-touch, sealing, or insulation features with a rigid structural core.
How Does the Overmolding LSR Injection Molding Process Work?
Step 1: Substrate Preparation
The base component (plastic, metal, or electronic insert) is:
- Injection molded separately or
- Inserted directly into the LSR mold
Common substrates include thermoplastics like PC, PBT, and metals such as stainless steel or aluminum.
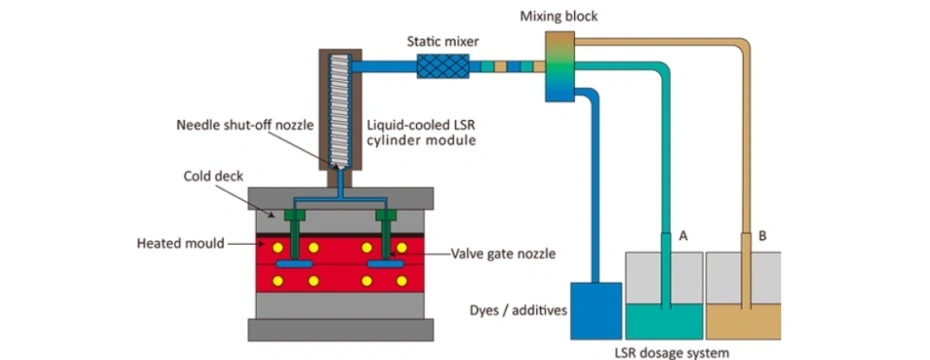
Step 2: LSR Material Mixing
LSR consists of:
- Part A (base polymer)
- Part B (curing agent)
These two components are:
- Metered at a 1:1 ratio
- Mixed precisely before injection
- Optionally combined with pigments or additives
Step 3: Injection into Heated Mold
The mixed LSR is injected into a heated mold cavity (typically 160–200°C), where:
- The silicone flows around the substrate
- Chemical crosslinking (vulcanization) begins immediately
Step 4: Curing and Bonding
LSR cures rapidly under heat, forming:
- A strong mechanical or chemical bond with the substrate
- Excellent sealing and encapsulation properties
No secondary bonding or adhesives are required.
Step 5: Demolding and Inspection
After curing:
- The finished overmolded part is demolded
- Flash is minimal or eliminated
- Parts undergo dimensional and functional inspection
For medical applications, this often occurs in ISO Class cleanrooms.
Key Advantages of LSR Overmolding Injection Molding
1. Strong Bonding Without Adhesives
LSR forms an excellent bond with many substrates, reducing:
- Assembly steps
- Risk of delamination
- Long-term failure
2. High Precision and Consistency
LSR injection molding offers:
- Tight tolerances
- Repeatable quality
- Automated production
Ideal for high-volume production.
3. Excellent Sealing and Protection
LSR provides:
- Waterproof and dustproof sealing
- Electrical insulation
- Vibration damping
This makes it perfect for electronics and automotive components.
4. Medical-Grade and Biocompatible
Medical-grade LSR is:
- Hypoallergenic
- Sterilization-resistant (steam, gamma, EtO)
- FDA, USP Class VI, and ISO 10993 compliant
5. Design Freedom
LSR overmolding allows:
- Soft-touch grips
- Integrated gaskets
- Complex geometries
All in one molded component.

Common Materials Used in LSR Overmolding
Compatible Substrates
LSR can be overmolded onto:
- Thermoplastics: PC, PA, PBT, PPS
- Metals: Stainless steel, aluminum
- Electronics: PCB assemblies, sensors
Surface treatment or primers may be used to enhance bonding.
Applications of Overmolding LSR Injection Molding
Medical Devices
- Seals and diaphragms
- Catheter components
- Wearable medical devices
- Surgical instrument grips
Automotive Industry
- Connector seals
- Sensor housings
- Grommets and vibration dampers
Consumer Electronics
- Waterproof buttons
- Shock-absorbing housings
- Cable strain reliefs
Industrial Products
- Sealing components
- Protective covers
- Ergonomic handles

Design Considerations for LSR Overmolding
To achieve optimal results, consider:
- Material compatibility
- Shrinkage differences
- Wall thickness uniformity
- Undercuts and bonding areas
- Vent and gate design
Early involvement of an experienced LSR molding supplier helps avoid costly redesigns.
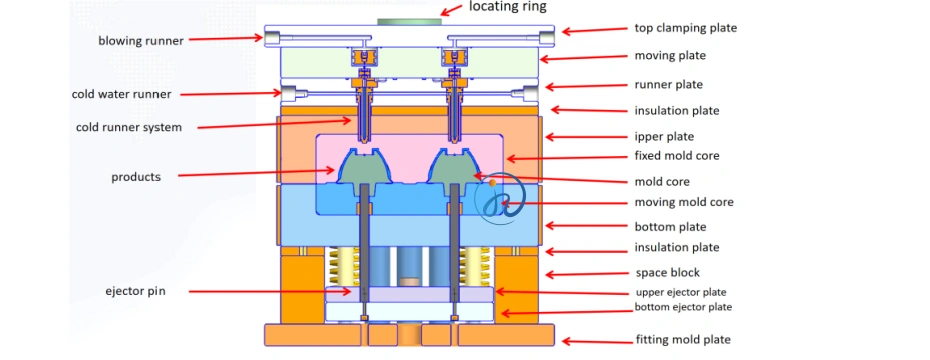
Cold Runner vs Hot Runner in LSR Overmolding
LSR overmolding can use:
- Cold runner systems for material savings
- Hot runner systems for high-volume efficiency
The choice depends on:
- Part complexity
- Production volume
- Cost considerations
Quality Control in LSR Overmolding
Key quality checks include:
- Bond strength testing
- Dimensional inspection
- Visual inspection for flash
- Functional testing (sealing, insulation)
Medical parts require full traceability and validation.
Why Choose LSR Overmolding for Your Project?
If your product requires:
- Multi-material integration
- Soft-touch or sealing features
- High durability and precision
- Medical or harsh-environment compliance
Then overmolding LSR injection molding is one of the most reliable and scalable manufacturing solutions available today.

Final Thoughts
The overmolding LSR injection molding process combines advanced material science with precision manufacturing to produce high-performance, multi-functional components.
By partnering with an experienced LSR injection molding manufacturer, you can achieve:
- Better product performance
- Reduced assembly costs
- Faster time to market
If you’re planning a project involving medical, automotive, or electronic LSR overmolding, early technical consultation is the key to success.