Table of Contents
ToggleLiquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) has become one of the most versatile elastomers in modern manufacturing. Its unique properties—such as biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and durability—make it an essential material for industries ranging from medical devices to automotive seals and baby care products.
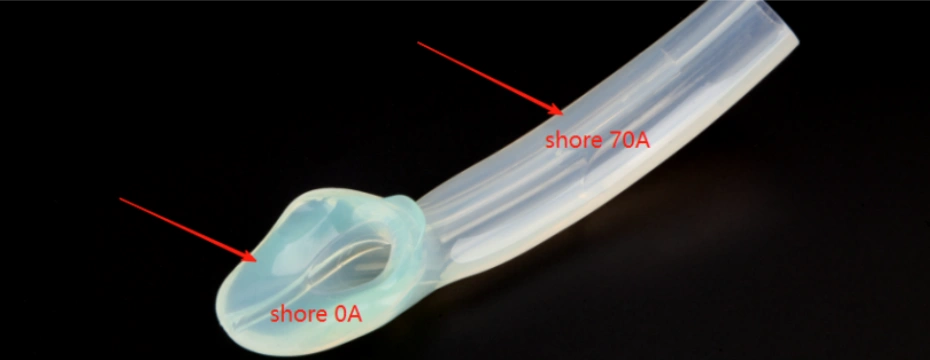
One of the most important characteristics of LSR that engineers and buyers must understand is its hardness. Hardness plays a critical role in determining how a silicone product feels, functions, and performs under real-world conditions. But what exactly does hardness mean in the context of liquid silicone rubber, and how is it measured?
This article explores the hardness of LSR, explains its measurement standards, factors that influence hardness, and guides you in choosing the right hardness for your applications.
1. Understanding Hardness in Liquid Silicone Rubber
Hardness refers to a material’s resistance to indentation or penetration. In elastomers like silicone, hardness indicates how soft or firm the material feels and how well it withstands mechanical stress.
For LSR, hardness is usually measured using the Shore A durometer scale. This standardized test helps manufacturers and buyers evaluate the flexibility, resilience, and suitability of silicone parts for specific applications.
2. How Hardness of LSR is Measured
The most common method is the Shore A hardness test:
- A durometer instrument presses a steel indenter into the surface of the silicone.
- The instrument measures the resistance to indentation.
- Results are displayed as a number from 0 (very soft) to 100 (extremely hard).
- Lower Shore A values (10–30): Soft, flexible, and gel-like LSRs.
- Medium Shore A values (40–60): Balanced hardness for versatile industrial applications.
- Higher Shore A values (70–80): Firm silicone suitable for durable seals and structural parts.
Some LSRs can also be measured on Shore 00 (softer than Shore A) or Shore D (harder plastics) depending on product needs.
3. The Typical Hardness Range of Liquid Silicone Rubber
Liquid silicone rubber usually falls within the 10 to 80 Shore A hardness range. This broad spectrum allows customization for different industries:
- 10–20 Shore A: Extremely soft, used in cushioning, wearable medical devices, and baby care products.
- 30–50 Shore A: Moderate hardness, common in seals, gaskets, and overmolded parts.
- 60–80 Shore A: Firm and strong, ideal for automotive components, industrial seals, and electrical connectors.
This flexibility makes LSR highly attractive for manufacturers who need precise material performance.
4. Factors That Influence LSR Hardness
Several factors affect the final hardness of an LSR product:
a) Material Formulation
Different curing agents, fillers, and additives can modify silicone hardness while maintaining other key properties like heat resistance or transparency.
b) Curing Conditions
Temperature, pressure, and curing time during injection molding directly affect the hardness outcome.
c) Design Requirements
Wall thickness, part geometry, and overmolding with plastics or metals can influence perceived hardness.
d) Post-Curing Treatment
Additional heat treatment can slightly alter hardness, improving mechanical stability and reducing volatiles for medical or food applications.
5. Why Hardness Matters in LSR Applications
The hardness of liquid silicone rubber determines:
- Comfort: In wearable devices or baby care products, softness ensures skin-friendliness.
- Durability: Harder grades resist mechanical wear, compression set, and environmental factors.
- Sealing Performance: Gaskets and O-rings must balance flexibility (to conform) with firmness (to resist deformation).
- Functionality: In optical or electronic components, the right hardness ensures dimensional stability and long-term performance.
Selecting the right hardness ensures a balance between comfort, strength, and reliability.
6. Applications of LSR by Hardness Level
Soft LSR (10–30 Shore A)
- Baby pacifiers, bottle nipples, and toys
- Wearable medical sensors
- Flexible cushioning pads
Medium LSR (40–60 Shore A)
- Automotive gaskets and seals
- Overmolded electronic parts
- Industrial connectors
Hard LSR (70–80 Shore A)
- High-performance seals in aerospace and automotive
- Medical valves and precision components
- Keypads and ruggedized housings

7. Choosing the Right Hardness for Your Project
When selecting LSR hardness, consider:
- Application environment (temperature, chemicals, stress cycles)
- Regulatory requirements (medical-grade vs. food-grade)
- User comfort and safety (especially for consumer-facing products)
- Production feasibility (mold design, cycle times, and costs)
Working closely with an experienced LSR manufacturer ensures the correct hardness is selected and consistently reproduced.
8. Testing and Quality Control of LSR Hardness
To guarantee product reliability, manufacturers use:
- Durometer testing (Shore A, 00, or D)
- Compression set testing (evaluates resistance to deformation)
- Tensile and elongation testing (measures strength and flexibility)
Maintaining strict quality standards ensures that the LSR parts meet the exact hardness requirements for their end use.

9. Future Trends in LSR Hardness Engineering
As industries evolve, manufacturers are developing custom LSR blends with tailored hardness for specific applications. For example:
- Medical implants: Super-soft LSRs with Shore A 10–20 for comfort.
- Electronics: Stable medium-hardness LSRs for reliable insulation.
- Automotive: High-hardness formulations for seals that endure extreme conditions.
Innovations in multi-hardness overmolding also allow products to combine soft-touch surfaces with rigid support in a single part.
Conclusion
The hardness of liquid silicone rubber is a fundamental property that determines how the material performs in diverse industries. With a wide range from 10 to 80 Shore A, LSR offers unmatched versatility—whether softness is needed for baby care products, or firmness is critical for automotive and medical applications.

By understanding how hardness is measured, what factors influence it, and how it impacts product performance, engineers and buyers can make smarter material choices. Partnering with a trusted LSR manufacturer ensures your products achieve the perfect balance of comfort, durability, and functionality.