Table of Contents
ToggleThe global demand for baby feeding products continues to grow rapidly, driven by rising birth rates in developing regions, increasing awareness of infant safety, and the popularity. Parents today are highly sensitive to material safety, hygiene, durability, and compliance with international standards.

For manufacturers, producing them is not just about molding plastic or silicone—it requires strict quality control, certified materials, compliant processes, and careful design.
In this guide, we will explain how to produce baby feeding products step by step, focusing on silicone-based items such as bottles, nipples, spoons, bibs, bowls, and teething feeders.
What Are Baby Feeding Products?
They are items designed to assist infants and toddlers during feeding stages, typically from newborn to 3 years old.
Common Baby Feeding Products Include:
- Baby bottles
- Silicone nipples and teats
- Baby spoons and forks
- Silicone bowls and plates
- Bibs
- Teething feeders
- Snack containers
- Training cups
Among these, liquid silicone rubber (LSR) and food-grade silicone have become the preferred materials due to their safety and flexibility.

Step 1: Product Design and Development
Understanding Market Requirements
Before production begins, manufacturers must understand:
- Target market (USA, EU, Australia, etc.)
- Applicable safety regulations
- Consumer usage habits
- Brand positioning (premium or mass market)
Design Considerations for Baby Feeding Products
- Smooth edges (no sharp corners)
- Ergonomic shape for baby hands
- Easy-to-clean structures
- Anti-choking and anti-spill designs
- Heat resistance for sterilization
Professional CAD software is usually used to create 3D product drawings for mold development.
Step 2: Material Selection (Critical for Safety)
Material choice is the most important factor in baby feeding product manufacturing.
Common Materials Used
Food-Grade Silicone
- BPA-free
- Non-toxic
- Odorless
- Temperature resistant (-40°C to 200°C)
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
- Platinum-cured
- Extremely pure
- Ideal for medical & baby products
- Excellent tear strength and elasticity
Why Silicone Is Preferred
- Does not release harmful chemicals
- Resistant to bacteria growth
- Can be sterilized repeatedly
- Soft and gentle on baby gums

Step 3: Mold Design and Tooling
Mold Design Principles
- Precision cavity design
- Balanced runner system
- Easy demolding
- High surface finish (mirror polishing)
For baby feeding products, LSR injection molds are widely used due to their high accuracy and cleanliness.
Types of Molds Used
- LSR injection molding molds
- Multi-cavity molds for mass production
High-quality mold steel ensures long mold life and consistent product quality.
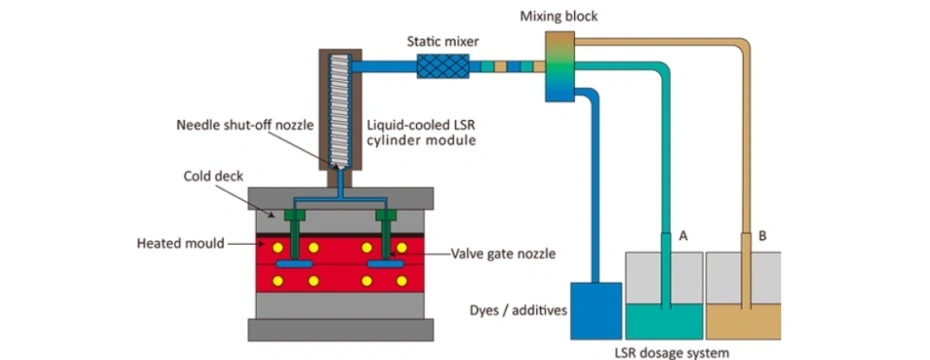
Step 4: Manufacturing Process of Baby Feeding Products
Silicone Baby Feeding Product Production Process
- Raw material mixing (LSR A & B components)
- Automatic dosing and injection
- Mold heating and curing
- Demolding
- Trimming (if required)
- Surface inspection
LSR injection molding is fully automated, reducing human contamination and improving consistency.
Step 5: Secondary Processing (If Required)
Some baby feeding products require additional processes:
- Overmolding with plastic (PP or PPSU)
- Printing or laser marking
- Assembly of multiple components
- Surface texture finishing
All secondary processes must remain food-safe and baby-safe.
Step 6: Cleaning and Post-Curing
To ensure product purity:
- Products are washed with purified water
- Post-curing removes volatile residues
- Controlled drying environments prevent contamination
This step is essential for FDA and LFGB compliance.
Step 7: Quality Control and Testing
Key Quality Control Procedures
- Visual inspection
- Dimension measurement
- Tear resistance testing
- Odor testing
- Heat resistance testing
Safety & Compliance Testing
It must comply with:
- FDA (USA)
- LFGB (Germany)
- EN14350 (EU baby bottle standard)
- CPSIA
- BPA / Phthalate-free requirements
Third-party lab testing is strongly recommended.

Step 8: Packaging
Packaging plays both protective and marketing roles.
Packaging Requirements
- Food-grade inner packaging
- Dust-free sealing
- Clear labeling
- Safety warnings
- Traceability information
Eco-friendly packaging is increasingly popular in global markets.
Step 9: Certifications and Documentation
To sell it internationally, manufacturers must provide:
- Material safety data sheets (MSDS)
- Test reports (FDA, LFGB)
- Production process documents
- Quality inspection records
Proper documentation builds trust with brands and distributors.
Common Challenges in Baby Feeding Product Manufacturing
Typical Issues Include:
- Material contamination
- Mold flashing
- Air bubbles
- Odor issues
- Inconsistent hardness
Working with an experienced silicone manufacturer significantly reduces these risks.
Why Choose Silicone for Baby Feeding Products?
Compared with plastic or rubber, silicone offers:
- Higher safety
- Better durability
- Superior flexibility
- Wider temperature tolerance
This is why premium brands worldwide prefer silicone baby feeding products.

Future Trends in Baby Feeding Products
- Sustainable materials
- Minimalist design
- Multi-functional products
- Custom colors and branding
- Smart feeding accessories
OEM and ODM manufacturers who innovate will remain competitive.
Conclusion
Producing baby feeding products requires more than manufacturing capability—it demands strict material control, precision molding, safety compliance, and professional quality management.
By using food-grade or liquid silicone rubber, advanced molding technology, and certified processes, manufacturers can deliver safe, reliable, and market-ready baby feeding products that meet global standards.
If you are looking to develop or source custom silicone baby feeding products, partnering with a professional silicone manufacturer is the key to long-term success.